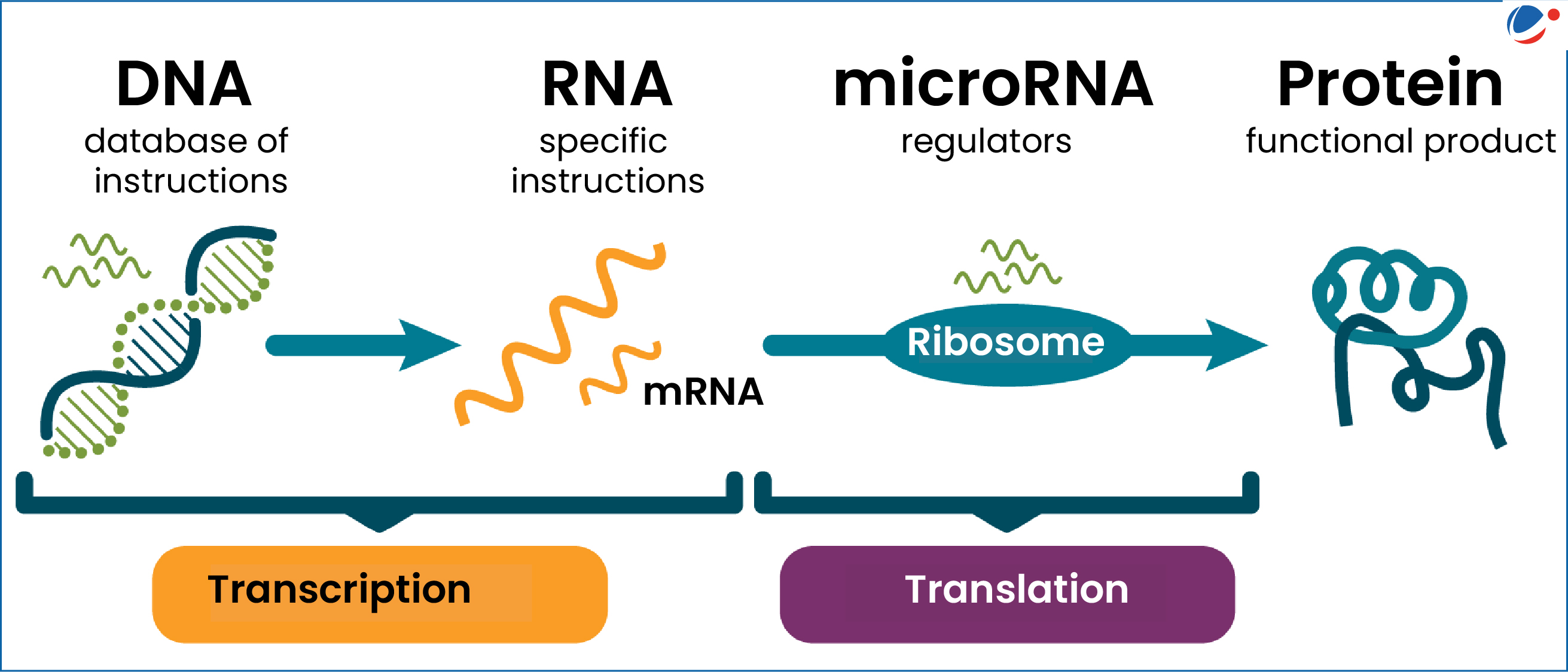
MicroRNA Research: The Journey to a Nobel Prize
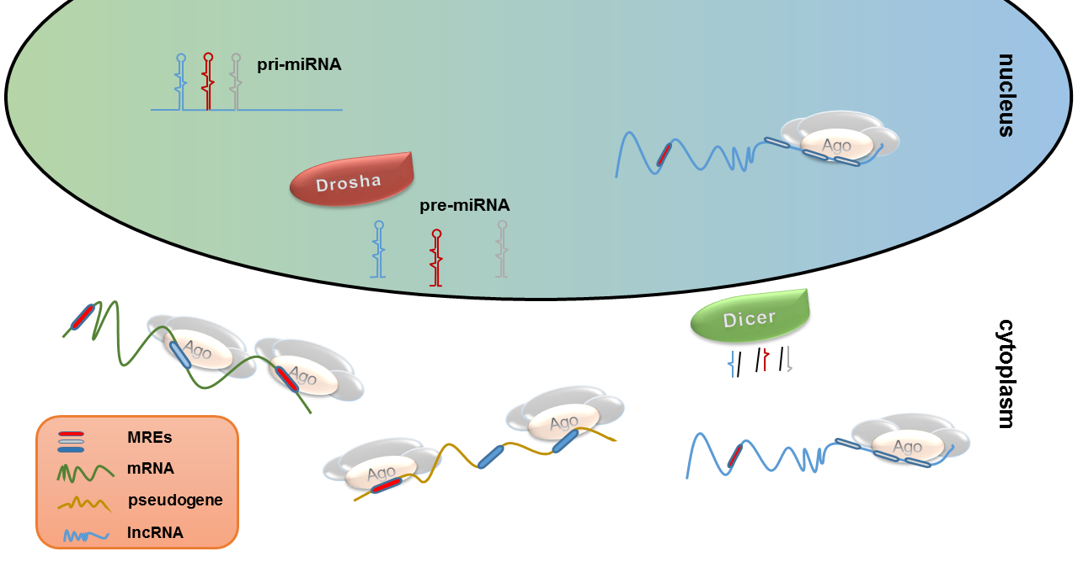
MicroRNA research has become a pivotal focus in modern biology, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms of gene regulation. Pioneering work by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun in the C. elegans model organism unveiled this revolutionary technology in the early 1990s, ultimately earning him recognition with the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Funded significantly by NIH grants, Ruvkun’s studies initially faced skepticism within the broader scientific community, but they have since catalyzed a burgeoning interest in the roles of microRNAs across various species, including humans. As researchers delve deeper, clinical trials are now exploring therapies leveraging microRNAs for diseases like heart conditions, cancer, and Alzheimer’s. The journey from a modest discovery to groundbreaking advancements demonstrates the profound impact of microRNA on our understanding of biology and medicine.
The exploration of small non-coding RNA molecules, particularly microRNAs, represents a revolutionary stride in the field of molecular genetics. Initially identified through studies on the roundworm C. elegans by groundbreaking scientists, including Gary Ruvkun, these tiny strands play a crucial role in modulating gene expression and have far-reaching implications for human health. While early observations were met with indifference, the evolving landscape of RNA research has unveiled their significance in regulating various biological processes. The surge of interest in this domain, fueled by substantial federal funding from institutions like the NIH, is paving the way for novel therapeutic strategies. As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities surrounding these small RNAs, the horizon for innovative treatments and understanding of genetic control expands dramatically.
The Groundbreaking Discovery of MicroRNA by Gary Ruvkun
In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and his collaborator Victor Ambros made a groundbreaking discovery that would lay the foundation for the field of microRNA research. Their work with the roundworm C. elegans revealed that these tiny RNA molecules play a crucial role in gene regulation. While at the time their findings did not garner immediate recognition, it became apparent later on that they had uncovered an innovative mechanism vital to understanding genetic expression in various organisms. This discovery would eventually lead to Ruvkun and Ambros receiving the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024, solidifying their contributions to molecular biology.
The significance of Ruvkun’s research extended beyond the small circle of the RNA research community. Initially, there was skepticism about whether microRNAs were relevant to significant biological processes in other species, including humans. However, as further studies emerged, it became clear that these small RNAs are essential for regulating the majority of protein-coding genes in the human genome, influencing a range of biological functions from development to disease progression.
Impact of NIH Grants on MicroRNA Advancement
Federal funding, particularly from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), played a pivotal role in advancing microRNA research and has significantly influenced the trajectory of Ruvkun’s work. Over the past 40 years, Ruvkun has relied on NIH grants to support his laboratory, which has allowed him to conduct innovative research and contribute to a growing field. With approximately three-quarters of his funding coming from federal sources, Ruvkun emphasizes the importance of sustained investment in scientific research to foster discoveries that can lead to commercial applications and therapeutic advancements.
The financial support from NIH has enabled Ruvkun and his team to explore various aspects of gene regulation and its potential implications for treating diseases. This research foundation has facilitated the emergence of pharmaceuticals aimed at conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s. By illustrating the direct correlation between government funding and groundbreaking scientific research, Ruvkun advocates for the continuous backing of similar initiatives to ensure that transformative science can continue to thrive.
C. elegans as a Model Organism in RNA Research
The choice of C. elegans as a model organism has been instrumental in the advancements of microRNA research. This roundworm, characterized by its simplicity and well-mapped genome, has provided a valuable platform for uncovering the complexities of genetic regulation. The insights gained from studying C. elegans have proven essential for translating findings to higher organisms, including humans. Ruvkun’s initial research set a precedent, encouraging a wave of scientists to investigate the role of microRNAs in various species, enriching our understanding of gene expression across biological systems.
Consequently, the findings from C. elegans have sparked a broader interest among researchers in fields beyond evolutionary biology, enhancing the overall significance of RNA studies. The worm community’s dedication to exploring these mutations in gene regulation has inspired a multitude of investigations, leading to numerous applications in biotechnology and medicine. As a result, C. elegans remains a cornerstone in the study of genetic control mechanisms.
Significance of MicroRNA Therapies in Modern Medicine
MicroRNA therapies are at the forefront of modern medicine, showcasing the remarkable potential of RNA in treating various diseases. Therapeutic strategies utilizing microRNAs are currently undergoing clinical trials for conditions like heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s disease, and Alzheimer’s. These promising approaches harness the power of microRNAs to modulate gene expression and combat pathological processes. As a result, these therapies are generating significant excitement in the biomedical community, proving that fundamental research can lead to tangible medical advancements.
With a deeper understanding of microRNA functions, scientists can create more targeted and effective treatment protocols. The ongoing clinical trials reflect a growing recognition that manipulating microRNA pathways can provide innovative solutions to previously challenging health issues. As research continues to evolve, the integration of microRNA-based therapies into mainstream medicine is expected to significantly enhance patient outcomes and revolutionize treatment paradigms.
The Evolution of Interest in MicroRNA Research
Since the initial discovery of microRNAs, there has been a substantial evolution in the interest surrounding this field of research. What began as a niche area, primarily supported by a dedicated community of RNA researchers, has burgeoned into a global scientific initiative. Conferences that once saw modest attendance have experienced exponential growth, reflecting the increasing recognition of microRNA’s pivotal role in gene regulation and associated diseases. This burgeoning interest has fostered collaboration across diverse fields, highlighting the interdisciplinary nature of current research.
The transition from obscurity to prominence for microRNA research underscores the dynamic nature of scientific discourse. As researchers continue to share their findings and explore the applications of microRNA in various domains, the field has garnered support from both public and private sectors. This convergence of interest not only stimulates further research but also inspires the next generation of scientists to contribute to this exciting arena of molecular biology.
Gary Ruvkun’s Vision for Future Scientific Inquiry
Reflecting on his illustrious career, Gary Ruvkun expresses a vision for the future of scientific inquiry that emphasizes the necessity of continued funding. He advocates for an ecosystem that nurtures innovation and supports young scientists pursuing research in areas with the potential for groundbreaking discoveries. Ruvkun’s insights into the challenges faced by the next generation underscore the importance of creating an environment conducive to scientific exploration and discovery. He worries that inequities in funding could push talented individuals away from research careers, reversing progress made in fields like microRNA.
Ruvkun’s dedication to foundational science demonstrates his belief in the long-term benefits of investing in research and education. By fostering an environment of curiosity and inquiry, he hopes to inspire future leaders in science capable of addressing pressing global challenges. The lessons learned from decades of microRNA research serve as a blueprint for the importance of perseverance, collaboration, and funding within the scientific community.
The Role of Federal Funding in Biomedical Research
Federal funding remains a cornerstone of biomedical research in the United States, significantly influencing the trajectories of scientific breakthroughs. Researchers, including Ruvkun, have heavily relied on grants from institutes like the NIH to sustain their projects and advance discoveries. This funding framework not only supports basic research needed for understanding complex biological phenomena but also underpins the development of innovative therapies that can ultimately benefit society. Ruvkun’s experiences highlight the critical role that government investment plays in transforming scientific ideas into real-world applications.
The success of Ruvkun’s research epitomizes how well-funded laboratories foster exceptional scientific talent and lead to significant advancements in knowledge. Continuous federal support aligns with robust national interests in maintaining a leadership position in global scientific innovation. By recognizing the reciprocating relationship between funding and discovery, stakeholders can advocate for policies that secure the future of biomedical research, ensuring continued progress and breakthroughs.
Commercialization of MicroRNA Discoveries
The transition from laboratory research to commercialization is vital for translating scientific discoveries into practical applications. Ruvkun is proud that his pioneering work has contributed to the establishment of successful pharmaceutical companies, such as Alnylam, which specializes in RNA interference therapeutics. The emergence of these companies underscores the potential of microRNA discoveries to address genetic diseases and other health challenges. This commercialization reflects a growing trend in science where basic research leads directly to transformative health solutions.
The establishment of biotech companies supports economic growth and job creation, further legitimizing investments in fundamental research. Ruvkun’s contributions not only advanced knowledge in gene regulation but paved the way for entrepreneurial ventures that leverage this knowledge for public benefit. The intertwined relationship between research, innovation, and commercialization exemplifies how scientific advancements can help shape a healthier future while simultaneously boosting the economy.
Global Perspectives on MicroRNA Research
MicroRNA research is not only a relevant subject within the U.S. but has also garnered international interest, fostering a collaborative global scientific community. Researchers around the world are increasingly acknowledging the significance of microRNAs in gene regulation, leading to cross-border collaboration that enhances research quality and impact. The exchange of knowledge and resources through international partnerships magnifies the potential for breakthroughs that benefit global populations, addressing health issues that transcend geographical boundaries.
As science continues to progress, it becomes evident that addressing complex biological challenges requires a unified approach. The collaborative nature of microRNA research exemplifies how shared objectives bring together experts from diverse backgrounds to create innovative solutions. By prioritizing interdisciplinary cooperation, the scientific community can accelerate the development of microRNA-based therapies, thus improving health outcomes on a broader scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did microRNA play in gene regulation as discovered by Gary Ruvkun?
MicroRNA plays a crucial role in gene regulation by modulating the translation of genes into proteins. Gary Ruvkun’s work, particularly in the model organism C. elegans, revealed how these tiny RNA molecules are pivotal in controlling various biological processes. This discovery has fundamentally reshaped our understanding of gene expression and regulation.
How did NIH grants contribute to the advancement of microRNA research?
NIH grants have been instrumental in advancing microRNA research, providing the necessary funding that has supported foundational studies in the field. Gary Ruvkun’s laboratory relied on these federal funds to explore gene regulation through microRNAs, leading to significant breakthroughs that gained attention and recognition within the scientific community.
What were the initial reactions to Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNA in C. elegans?
Initially, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros’s discovery of microRNA in C. elegans was met with skepticism from the evolutionary biology community. Their findings, published in 1993, showcased a new level of gene regulation, but the significance of microRNAs for other species, including humans, was not immediately appreciated.
What are the current applications of microRNA research in medicine?
Current applications of microRNA research in medicine include therapies aimed at treating various diseases such as heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s disease, and Alzheimer’s. Many of these therapies are undergoing clinical trials, showcasing the potential of microRNA to revolutionize treatment options and improve patient outcomes.
How has the perception of microRNA research changed over the years?
The perception of microRNA research has dramatically changed from initial skepticism to widespread recognition of its significance in gene regulation. Over the years, increased interest and funding, particularly from NIH grants, have led to major advancements in understanding microRNA functions across different organisms, making it a hot topic in molecular biology.
What impact has microRNA research had on pharmaceutical developments?
MicroRNA research has had a profound impact on pharmaceutical developments, leading to the creation of companies like Alnylam, which focuses on RNA interference therapeutics. The foundational discoveries made by researchers like Gary Ruvkun have facilitated significant advancements in treating genetic diseases and developing innovative RNA-based therapies.
Why is federal funding crucial for microRNA research, according to Gary Ruvkun?
According to Gary Ruvkun, federal funding is crucial for microRNA research as it supports the basic science necessary for groundbreaking discoveries. He emphasizes that this funding not only sustains research labs but also contributes to the health of the broader scientific community and, ultimately, economic growth through innovation.
What future directions does microRNA research hold?
Future directions for microRNA research include exploring their roles in additional diseases, understanding their complex interactions within biological systems, and developing targeted therapies. As new technologies and methodologies emerge, this field is likely to continue providing insights that could lead to novel clinical applications and improved therapeutic strategies.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in C. elegans, recognized later with the 2024 Nobel Prize. |
| Initial Reception | Their findings initially received little acclaim, with significant attention coming later from RNA researchers. |
| Impact on Research | MicroRNAs are now viewed as critical in gene regulation, influencing protein production in humans and other organisms. |
| Federal Funding | Ruvkun attributes 75% of his lab funding from federal sources, emphasizing the importance of sustained investment in scientific research. |
| Clinical Trials | Therapies involving microRNAs are currently being tested for various diseases including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. |
| Economic Impact | Ruvkun highlights that foundational research has led to the creation of successful companies like Alnylam, aiding technological advancements in medicine. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has emerged as a pivotal area in biological science, reshaping our understanding of gene regulation. Initially discovered by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in 1992, microRNAs are now recognized for their critical roles in the development and function of organisms. Their impact is profound, with ongoing clinical trials aiming to harness their therapeutic potential for diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. The sustained federal funding that supports this research underscores the importance of governmental investment in science, fostering innovation and economic growth. As the field continues to evolve, the implications of microRNA research promise to revolutionize approaches to healthcare and biotechnology.